Spatial Guide
Phidget Spatials combine data from accelerometers, magneometers, and gyroscopes into one sensor. This guide explains how the sensors are combined using AHRS, what you can do with this data.
The PhidgetSpatial 3/3/3 combines the functionality of a 3-axis compass, a 3-axis gyroscope, and a 3-axis accelerometer all in one convenient package. It's less expensive than our other spatial devices, and is ideal for applications where it's more important to know the general motion of an object rather than the precise amounts.
Use a USB cable to connect this Phidget to your computer. We have a number of different lengths available, although the maximum length of a USB cable is 5 meters due to limitations in the timing protocol. For longer distances, we recommend that you use a Single Board Computer to control the Phidget remotely.
| Product | Physical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part Number | Price | Connector A | Connector B | Cable Length |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 28cm 24AWG
|
$3.00 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B | 280 mm |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 28cm Right Angle
|
$3.50 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B (90 degree) | 280 mm |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 60cm 24AWG
|
$3.50 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B | 600 mm |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 83cm Right Angle
|
$4.50 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B (90 degree) | 830 mm |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 120cm 24AWG
|
$4.00 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B | 1.2 m |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 180cm 24AWG
|
$4.00 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B | 1.8 m |
 USB-A to Mini-B Cable 450cm, 20 AWG 2C
|
$12.00 | USB Type A | USB Mini-B | 4.5 m |
 USB-C to Mini-B Cable 60cm 24AWG
|
$5.00 | USB Type C | USB Mini-B | 600 mm |
 USB-C to Mini-B Cable 180cm 24AWG
|
$6.00 | USB Type C | USB Mini-B | 1.8 m |
Welcome to the 1042 user guide! In order to get started, make sure you have the following hardware on hand:
Next, you will need to connect the pieces:

Now that you have everything together, let's start using the 1042!
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1042, the Phidget Control Panel running on a Windows machine will be used.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines.
To open the Phidget Control Panel on Windows, find the ![]() icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
To open the Phidget Control Panel on macOS, open Finder and navigate to the Phidget Control Panel in the Applications list. Double click on the ![]() icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
For more information, take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1042.
After plugging the 1042 into your computer and opening the Phidget Control Panel, you will see something like this:
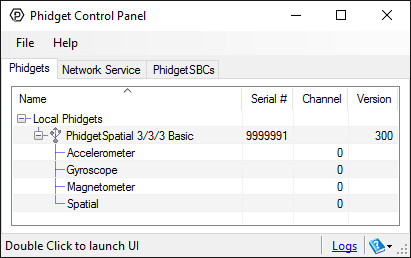
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Double-click on the Accelerometer object in order to run the example:
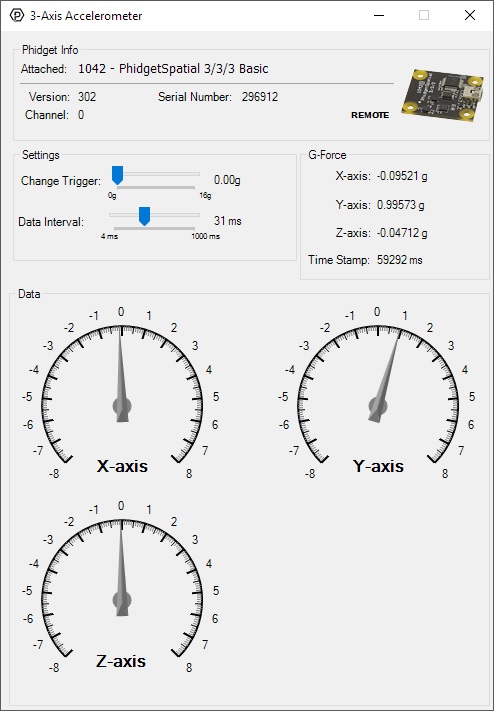
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
Double-click on the Gyroscope object in order to run the example:
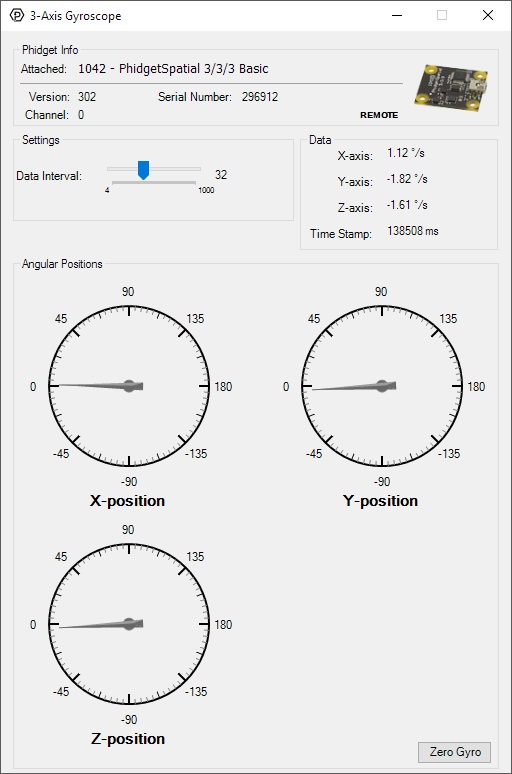
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
Double-click on the Magnetometer object in order to run the example:
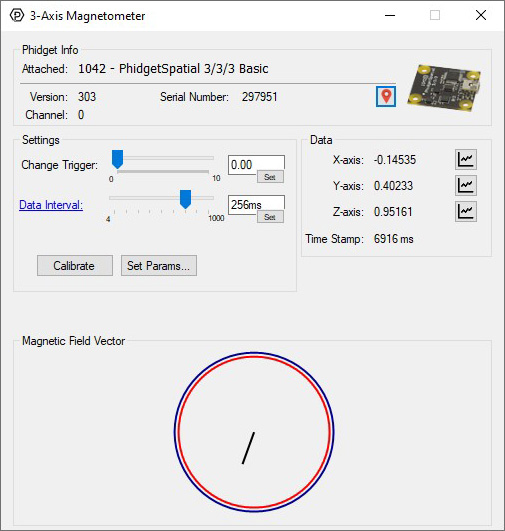
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
Double-click on the Spatial object in order to run the example:
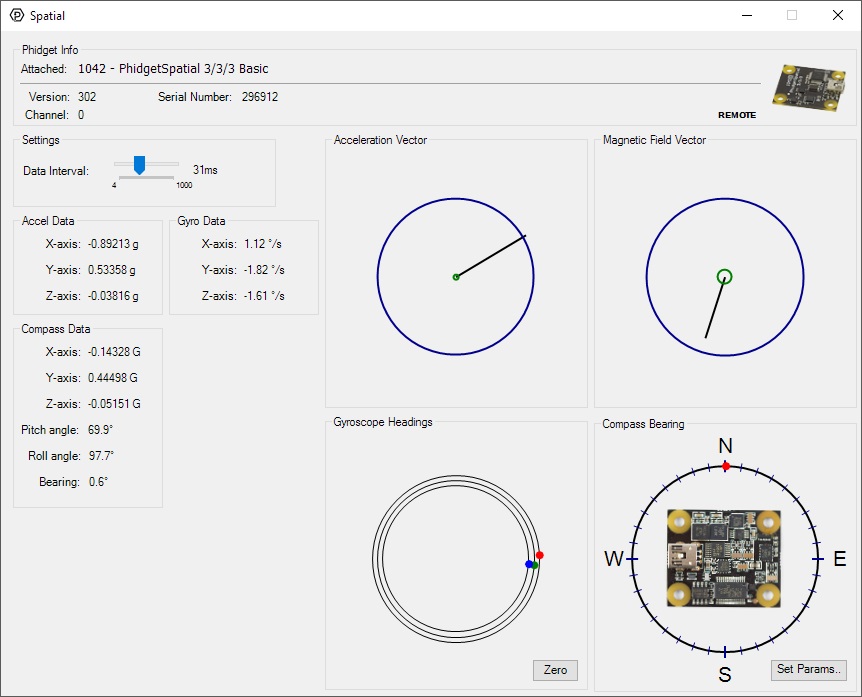
The Spatial example demonstrates that you can receive data from the accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer all at once by using the Spatial object rather than the other three objects individually.
Before you can access the device in your own code, and from our examples, you'll need to take note of the addressing parameters for your Phidget. These will indicate how the Phidget is physically connected to your application. For simplicity, these parameters can be found by clicking the button at the top of the Control Panel example for that Phidget.
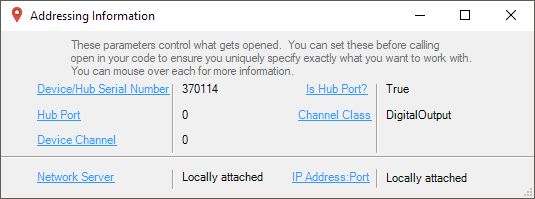
In the Addressing Information window, the section above the line displays information you will need to connect to your Phidget from any application. In particular, note the Channel Class field as this will be the API you will need to use with your Phidget, and the type of example you should use to get started with it. The section below the line provides information about the network the Phidget is connected on if it is attached remotely. Keep track of these parameters moving forward, as you will need them once you start running our examples or your own code.
You are now ready to start writing your own code for the device. The best way to do that is to start from our Code Samples.
Select your programming language of choice from the drop-down list to get an example for your device. You can use the options provided to further customize the example to best suit your needs.
Once you have your example, you will need to follow the instructions on the page for your programming language to get it running. To find these instructions, select your programming language from the Programming Languages page.
The 1042 has a 3-Axis accelerometer that can measure ±8 g (±78 m/s2) per axis. It will measure both dynamic acceleration (change in velocity) and static acceleration (gravity vector).
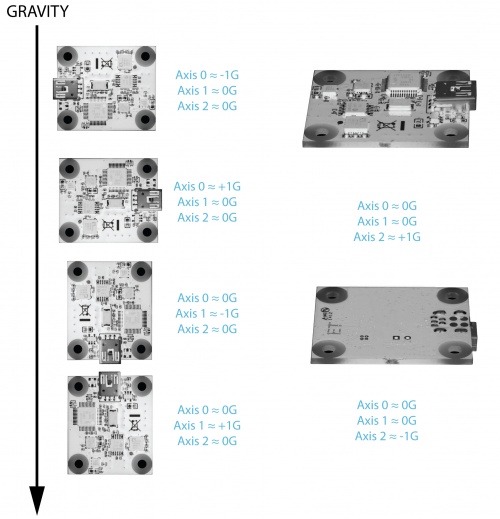
When working with an accelerometer it is important to know which is the positive and negative direction on each of the axes. This can be determined by orienting the accelerometer along each axis and checking the output. The above image shows what the axis readings should be for each orientation of the 1042.
For more information on how to use the accelerometer, check the Accelerometer Guide.
For more information on the gyroscope, see the Gyroscope Guide.
The magnetometer reports the sum of all magnetic fields acting on the 1042. The Earth's magnetic field is only one source that affects this measurement. In order to get accurate bearing data from the magnetometer ( i.e. to find magnetic north as a compass) any interfering magnetic effects need to be calibrated out. For more information about calibration, see the section below, or the Magnetometer Guide.
Any magnetic field that is stationary with respect to the 1042, and less than ± 3 Gauss, can be calibrated out of the magnetic field measurement. This includes both hard and soft iron effects caused by nearby ferrous and magnetic materials. Interfering magnetic fields that vary in strength and orientation with respect to the 1042 can not be easily calibrated out.
Magnetic field data will become unavailable during every other sample as the compass performs internal calibrations. When this happens, the magneticField array in the SpatialData structure will either have a length of zero, or each element will equal PUNK_DBL, depending on the API being used. This needs to be handled explicitly in the event handling code to avoid erroneous program behavior. The maximum sampling rate of the compass is 125 Hz.
For more information on magnetometers (compasses), see the Magnetometer Guide.
| Accelerometer | |
|---|---|
| Acceleration Measurement Max | ± 8 g |
| Acceleration Measurement Resolution | 976.7 μg |
| Accelerometer White Noise σ | 2.8 mg |
| Accelerometer Minimum Drift σ | 1.9 mg |
| Accelerometer Optimal Averaging Period | 286 s |
| Gyroscope | |
| Gyroscope Speed Max | ± 2000°/s |
| Gyroscope Resolution | 0.07°/s |
| Gyroscope White Noise σ | 0.59°/s |
| Gryoscope Minimum Drift σ | 0.0019°/s |
| Gyroscope Optimal Averaging Period | 8628 s |
| Magnetometer | |
| Magnetic Field Max | 5.5 G |
| Magnetometer Resolution | 3 mG |
| Magnetometer White Noise σ | 1.2 mG |
| Magnetometer Minimum Drift σ | 87 μG |
| Board Properties | |
| Controlled By | USB (Mini-USB) |
| USB Stack | HID |
| Driver Support | Phidget21, Phidget22 |
| API Object Name | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Magnetometer |
| Current Consumption Max | 40 mA |
| Sampling Speed Min | 1 s/sample |
| Sampling Speed Max | 4 ms/sample |
| Sampling Speed Min (Webservice) | 1 s/sample |
| Sampling Speed Max (Webservice) | 12 ms/sample |
| USB Voltage Min | 4.4 V DC |
| USB Voltage Max | 5.3 V DC |
| USB Speed | Full Speed |
| Operating Temperature Min | -40 °C |
| Operating Temperature Max | 85 °C |
| Customs Information | |
| Canadian HS Export Code | 8471.80.00 |
| American HTS Import Code | 8471.80.40.00 |
| Country of Origin | CN (China) |
| Date | Board Revision | Device Version | Packaging Revision | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 2012 | 0 | 300 | Product Release | |
| September 2012 | 0 | 301 | Fixed USB bug | |
| October 2015 | 0 | 302 | OS X El Capitan USB fix | |
| February 2016 | 0 | 303 | Fixed issue that prevented gyroscope from working | |
| January 2018 | 0 | 303 | B | Added plastic shell enclosure and removed USB cable |
| Channel Name | API | Channel |
|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis Accelerometer | Accelerometer | 0 |
| 3-Axis Gyroscope | Gyroscope | 0 |
| 3-Axis Magnetometer | Magnetometer | 0 |
| Spatial | Spatial | 0 |
Use the following program to correct for magnetic errors in your application:
| API | Detail | Language | OS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerometer | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| Accelerometer | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| Accelerometer | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| Accelerometer | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| Accelerometer | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| Accelerometer | Max | Multiple | Download | |
| Gyroscope | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| Gyroscope | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| Gyroscope | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| Gyroscope | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| Gyroscope | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| Gyroscope | Max | Multiple | Download | |
| Magnetometer | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| Magnetometer | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| Magnetometer | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| Magnetometer | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| Magnetometer | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| Magnetometer | Max | Multiple | Download | |
| Spatial | Compass Calibrator | C | Multiple | Download |
| Spatial | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| Spatial | Compass Calibrator | C# | Windows | Download |
| Spatial | Spatial AHRS/IMU | C# | Windows | Download |
| Spatial | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| Spatial | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| Spatial | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| Spatial | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| Spatial | Max | Multiple | Download |
| Product | Accelerometer | Gyroscope | Magnetometer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part Number | Price | Acceleration Measurement Max | Acceleration Measurement Resolution | Gyroscope Resolution | Gyroscope Angular Rate Max | Magnetic Field Max | Magnetometer Resolution |
 PhidgetSpatial Precision 3/3/3
|
$105.00 | ± 16 g | 30 μg | 0.004°/s | ± 2000°/s | ± 8 G | 1.5 mG |
 PhidgetAccelerometer
|
$40.00 | ± 8 g | 250 μg | — | — | — | — |
 Spatial Phidget
|
$32.00 | ± 8 g | 250 μg | 0.07°/s | ± 2000°/s | ± 8 G | 1.5 mG |
 Accelerometer Phidget
|
$20.00 | ± 8 g | 1 mg | — | — | — | — |
 PhidgetSpatial Precision 0/0/3 High Resolution
|
$80.00 | ± 2 g | 76.3 μg | — | — | — | — |