In this step, you will learn how to measure your scale's offset.

You will need to create a new project called PhidgetScale and import the Phidgets Library. If you’ve forgotten how to do this, revisit the Configure section from the Getting Started Kit.
Write Code (Java)
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples.
package phidgetscale;
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
public class PhidgetScale {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//Create
VoltageRatioInput scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
//Open
scale.open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while(true){
System.out.println("Offset Value: " + scale.getVoltageRatio());
Thread.sleep(250);
}
}
}
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
public class PhidgetScale {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//Create
VoltageRatioInput scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
//Open
scale.open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while(true){
System.out.println("Offset Value: " + scale.getVoltageRatio());
Thread.sleep(250);
}
}
}
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
//Define
VoltageRatioInput scale;
void setup(){
try{
//Create
scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
//Open
scale.open(1000);
}catch(Exception e){
//Handle Exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
void draw(){
try{
//Use your Phidgets
println("Offset Value: " + scale.getVoltageRatio());
delay(250);
}catch(Exception e){
//Handle Exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Write Code (Python)
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples.
#Add Phidgets Library
from Phidget22.Phidget import *
from Phidget22.Devices.VoltageRatioInput import *
#Required for sleep statement
import time
#Create
scale = VoltageRatioInput()
#open
scale.openWaitForAttachment(1000)
#Use your Phidgets
while(True):
print("Offset Value: " + str(scale.getVoltageRatio()))
time.sleep(0.25)
Write Code (C#)
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples.
//Add Phidgets Library
using Phidget22;
namespace PhidgetScale
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create
VoltageRatioInput scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
//Open
scale.Open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while (true)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("Offset Value: " + scale.VoltageRatio);
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(250);
}
}
}
}
Write Code (Swift)
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples.
The code below assumes you've created a single label and linked it to an IBOutlet named offsetLabel
import Cocoa
//Add Phidgets Library
import Phidget22Swift
class ViewController: NSViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var offsetLabel: NSTextField!
//Create
let scale = VoltageRatioInput()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
do{
//Subscribe to event
let _ = scale.voltageRatioChange.addHandler(scale_change)
//Open
try scale.open()
}catch{
print(error)
}
}
func scale_change(sender:VoltageRatioInput, voltageRatio: Double){
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Use your Phidget
self.offsetLabel.stringValue = String(voltageRatio)
}
}
}
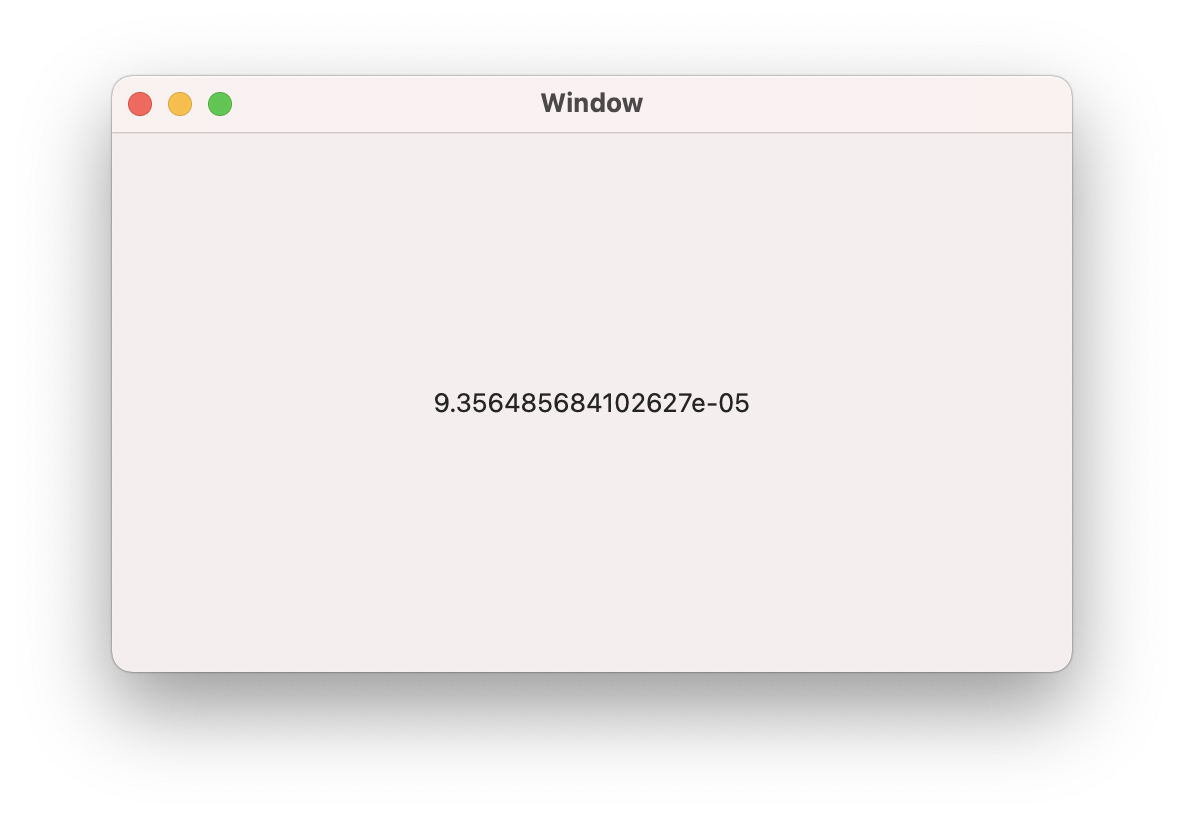
Run Your Program
The default value coming from your scale is called the offset. With a bit of math in the next section, you will convert the value into a weight. For now, you can try lightly pushing on the scale to see the measurement change.
What Is an Offset?
When your scale has nothing on it, you would expect the output to be 0. In reality, there's a small offset associated with the load cell itself, and the scale assembly that's sitting on top of the load cell. This is called the offset, and it must be subtracted from future measurements in order to obtain accurate readings.
Collect Values
Using your program, determine the offset of your scale. Your program will display multiple values for offset that are very close together, simply pick one and write the value down.
| Scale Offset | ? |
|---|
Make sure to write the value down, you will need it in the section!