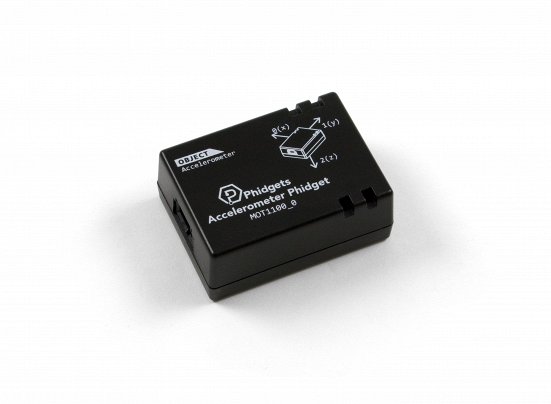
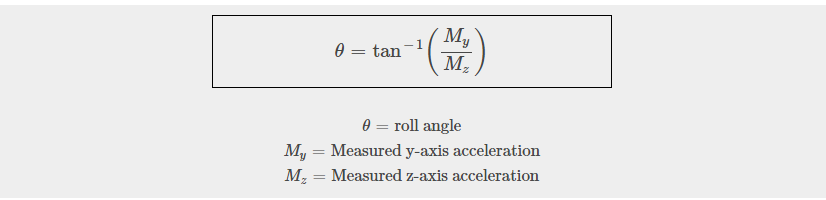Setup
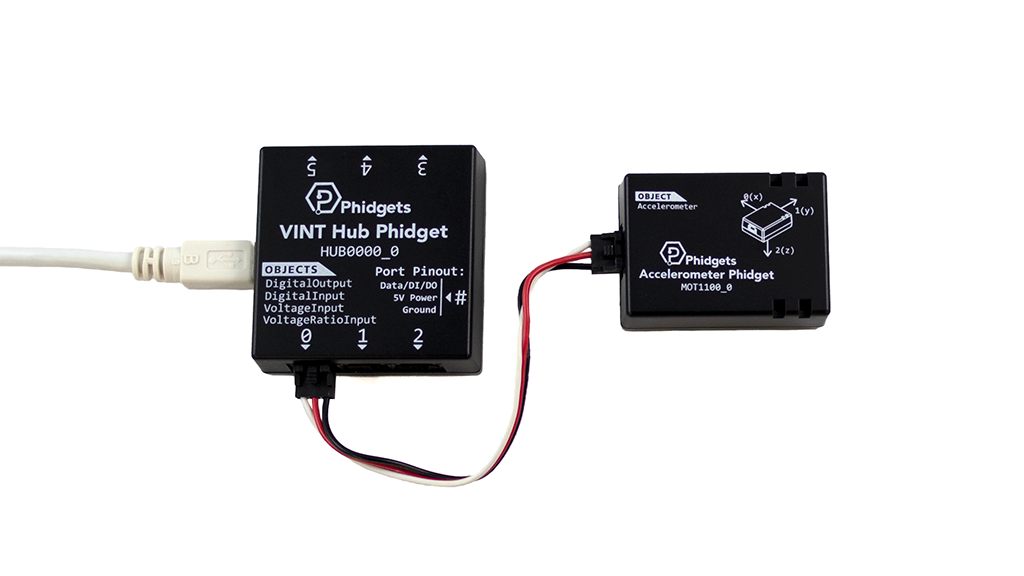
Before getting started, make sure you have the following parts.
Note: you can also use the Phidget Spatial or any Phidget with an accelerometer for this project.
VINT Hub

Write code (Java)
Copy the code below into a new Java project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course. Insert the code below.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
public class DigitalLevel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create
Accelerometer acceleration = new Accelerometer();
//Open
acceleration.open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while (true) {
//Get axis information
double x = acceleration.getAcceleration()[0];
double y = acceleration.getAcceleration()[1];
double z = acceleration.getAcceleration()[2];
//Calculate tilt angles
double pitch = Math.round(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan(x / z)));
double roll = Math.round(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan(y / z)));
System.out.println("Pitch: " + pitch + "°, Roll: " + roll + "°");
Thread.sleep(150);
}
}
}
package digitallevel;
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
public class DigitalLevel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create
Accelerometer acceleration = new Accelerometer();
//Open
acceleration.open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while (true) {
//Get axis information
double x = acceleration.getAcceleration()[0];
double y = acceleration.getAcceleration()[1];
double z = acceleration.getAcceleration()[2];
//Calculate tilt angles
double pitch = Math.round(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan(x / z)));
double roll = Math.round(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan(y / z)));
System.out.println("Pitch: " + pitch + "°, Roll: " + roll + "°");
Thread.sleep(150);
}
}
}
Write code (Python)
Copy the code below into a new Python project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course. Insert the code below.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
#Add Phidgets library
from Phidget22.Phidget import *
from Phidget22.Devices.Accelerometer import *
#Required for sleep statement
import time
#Required for atan
import math
#Create
accel = Accelerometer()
#Open
accel.openWaitForAttachment(1000)
#Use your Phidgets
while (True):
#Get axes information
x = accel.getAcceleration()[0]
y = accel.getAcceleration()[1]
z = accel.getAcceleration()[2]
#Calculate tilt angles
pitch = round(math.degrees(math.atan(x/z)))
roll = round(math.degrees(math.atan(y/z)))
print("Pitch: " + str(pitch) + "°, Roll: " + str(roll) + "°")
time.sleep(0.15)
Write code (C#)
Copy the code below into a new C# project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course. Insert the code below.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
//Add Phidgets Library
using System;
using Phidget22;
namespace Level
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create
Accelerometer accel = new Accelerometer();
//Open
accel.Open(1000);
//Use your Phidgets
while (true)
{
// Get x,y,z acceleration
double x = accel.Acceleration[0];
double y = accel.Acceleration[1];
double z = accel.Acceleration[2];
//calculate tilt angles
double pitch = Math.Round((Math.Atan(x / z)) * (180.0 / Math.PI));
double roll = Math.Round((Math.Atan(y / z)) * (180.0 / Math.PI));
System.Console.WriteLine("Pitch: " + pitch + " degrees, Roll: " +roll + " degrees");
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(150);
}
}
}
}
Write code (Swift)
Copy the code below into a new Swift project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course. Insert the code below.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
import Cocoa
//Add Phidget Library
import Phidget22Swift
class ViewController: NSViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var xLabel: NSTextField!
@IBOutlet weak var yLabel: NSTextField!
//Create
let accelerometer = Accelerometer()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
do{
//Subscribe to event
let _ = accelerometer.accelerationChange.addHandler(onAccelerationChange)
//Open
try accelerometer.open()
}catch{
print(error)
}
}
func onAccelerationChange(sender:Accelerometer, data: (acceleration:[Double], timestamp: Double)){
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Use information from your Phidget to change label
let x = data.acceleration[0]
let y = data.acceleration[1]
let z = data.acceleration[2]
let roll = atan(y/z)*180/Double.pi
let pitch = atan(x/z)*180/Double.pi
self.xLabel.stringValue = "Roll: " + String(roll) + " °"
self.yLabel.stringValue = "Pitch: " + String(pitch) + " °"
}
}
}
Run your program. When tilting your device, you will see the angle output change.
Tilt Angles
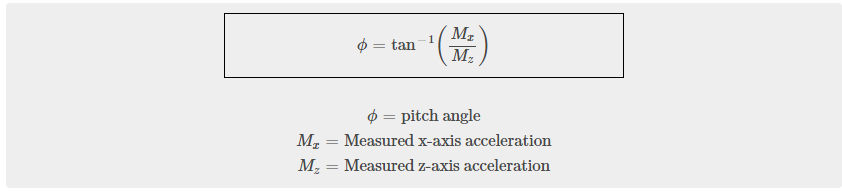
In the code above we calculated two tilt angles Roll and Pitch.
Pitch
Pitch is the side to side movement.

Roll
Roll is the forward and backward movement.

Tilt Angles contd.
Acceleration values in the three axis change as you move accelerometer. When the accelerometer is level or at rest, the x axis acceleration is 0, the y axis acceleration is 0, and the z axis acceleration is 1. We can use the acceleration values to calculate the angle the accelerometer is at compared to the rest position.
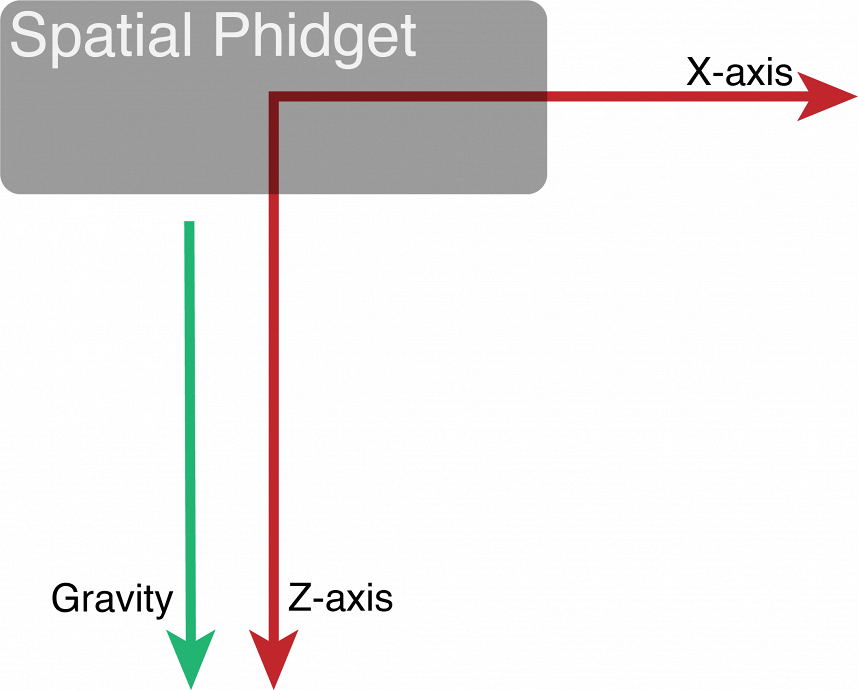
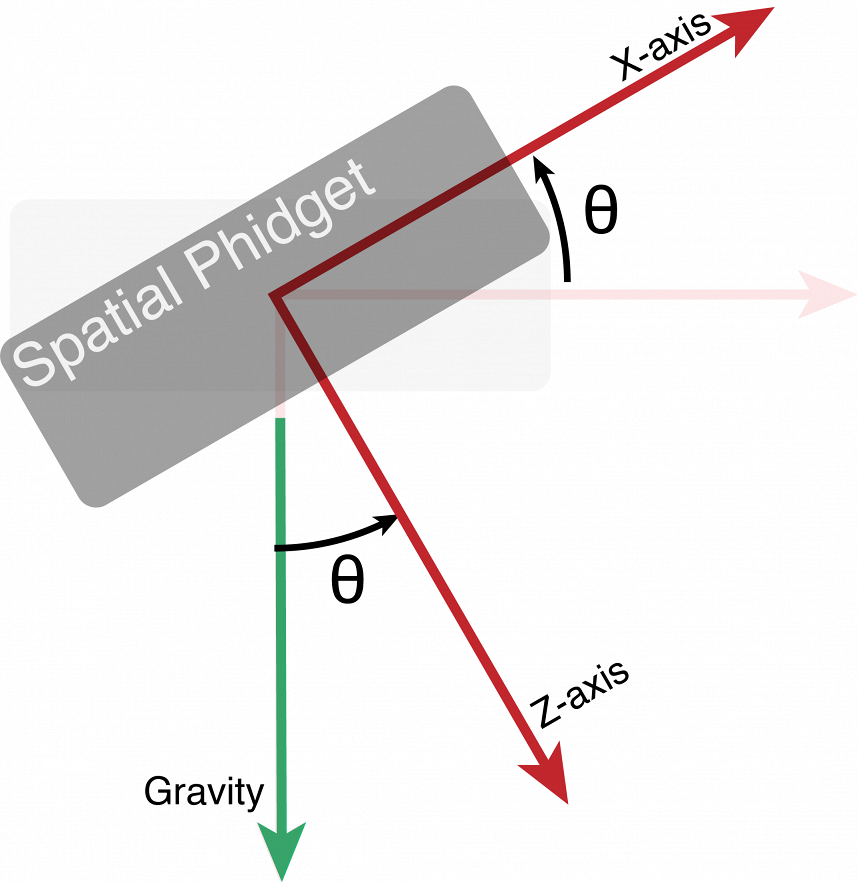
Practice
- Create a level using your accelerometer and tilt angles. If the Roll and Pitch are between -2 and 2 degrees, print “Object level”. Otherwise print the angles to the user.
- If you are able to create a graphical program (for example, using Processing, Pygame, etc.), try creating a visual aspect to the level. Similar programs are available on the iPhone (shown below).