What is VINT?
Introduction
VINT stands for Versatile Interface and it is the system that all modern Phidgets use to communicate.
The system is built around VINT Hubs. A VINT Hub allows you to connect VINT devices to your computer. Every VINT port on a VINT Hub can also be used independently as an analog input, digital input or digital output.
The main advantages of VINT are versatility, stability, and connectivity.
Versatility
As mentioned above, VINT Hub ports are capable of functioning as analog inputs, digital inputs, and digital outputs—simply select your mode in software and go. This allows you to tailor your system to your exact needs.
VINT Device Mode
This mode is for connecting to a VINT device. The VINT Hub and VINT device communicate using a digital protocol. | |
Digital Input Mode
In digital input mode, the VINT Hub port can act as an active-low digital input. This mode is great for reading the state of buttons, switches, and any other logic-level input. |
Voltage Ratio Input Mode
In voltage ratio input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire and compare it to the voltage supplied on the red wire. This mode will let you read any ratiometric Phidget sensor. |
Voltage Input Mode
In voltage input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire. This can be used to interface a non-ratiometric sensor or to measure the voltage in a 5V digital circuit. |
Digital Output Mode
In digital output mode, a VINT Hub port can behave like a 3.3V digital output. You could use this mode to blink an LED or switch on a MOSFET. |
Stability
Normally, an analog sensor operates by measuring its surroundings, converting that measurement into a voltage between 0 and 5 volts, and pulling its data line up to that voltage. The advantage of a system like this is that it's simple and usually compatible with other systems. One major downside, however, is how vulnerable this signal is to electromagnetic interference. A strong magnetic field produced by a running motor, the arc on a mechanical relay, or other mechanisms in the system can push the voltage on the data line up and down, resulting in inaccurate data.
VINT avoids this problem by communicating using a digital protocol rather than an analog voltage. If the electromagnetic interference is severe, the sensor may drop a data packet or two, but will soon resume sending data. This way, you can be sure that any data you receive is unaffected by interference.
Many VINT devices also have built-in data and power isolation to prevent power fluctuations from entering the system. Power fluctuations can cause unreliability by distorting reference values and in serious cases, damage parts of the system. These kinds of problems normally occur when multiple devices are powered by the same supply and current from the ground of one device enters other systems, or generally any application where small, sensitive components and high-power electronics need to coexist in the same system. An attached VINT device that has isolation built-in can be thought of as an entirely separate circuit, because power is provided via a small transformer, and data is transmitted with an opto-coupler.
Connectivity
Prior to the introduction of VINT, larger Phidget systems tended to sprawl, taking up several USB ports and sometimes causing reach problems due to USB cable length restrictions (5-meter maximum).
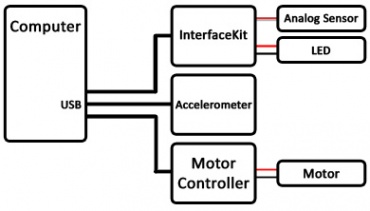

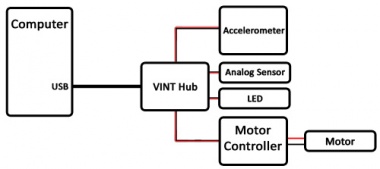
With newer VINT systems, fewer USB ports are required, and devices can extend up to 50 meters from a VINT Hub.