Language - Python: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (213 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{#seo:|description=Learn how to use Phidget USB devices with Python.}} | |||
[[Category:Language]] | |||
== | ==Get Started== | ||
With the Phidget22 Python library, it's easy to create Python applications that work with Phidget devices. | |||
== | ==Python Libraries== | ||
Python | ===pip Package=== | ||
The Phidget22 Python library is available as a [https://pypi.org/project/phidget22/ pip package]. Most development environments provide built-in tools to manage packages. View the [[#Development Environment Configuration | Development Environment Configuration]] section below for examples. | |||
====macOS Considerations==== | |||
Phidget devices running a HID USB stack require the installation of the macOS libraries or the standalone Phidget Control Panel ([{{SERVER}}/docs/OS_-_macOS download here]). | |||
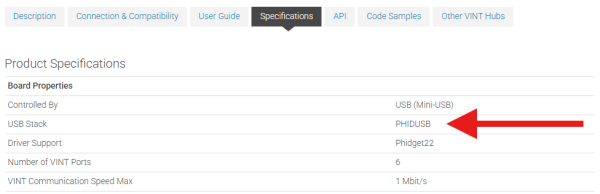
To determine what USB stack your Phidget device is on, navigate to the product page and then to the specification tab, and look for the ''USB Stack'' specification. If you are using a VINT device, navigate to the product page for the VINT Hub you are using. | |||
= | [[Image:Javascript_networkserver_webusb_spec.png|center|600px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/8/80/Javascript_networkserver_webusb_spec.png]] | ||
====Linux Considerations==== | |||
Linux restricts access to USB devices to the root user. To run your Python application as a regular user, you'll need to [{{SERVER}}/docs/OS_-_Linux#Setting_Udev_Rules set up udev rules] on your system. | |||
== | ===Source Files=== | ||
The Phidget22 Python library source files are available [https://cdn.phidgets.com/downloads/phidget22/libraries/any/Phidget22Python.zip here]. | |||
==Development Environment Configuration== | |||
Most development environments provide built-in tools to manage Python interpreters, packages, and virtual environments. See the examples below for more information. | |||
===Installing a Python Interpreter=== | |||
If you don't already have a Python interpreter installed, you can download and install one from [https://www.python.org/downloads/ python.org] or through package managers like [https://brew.sh/ Homebrew]. | |||
== | ===Visual Studio Code=== | ||
{| style="margin:auto;" class="table-no-border mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
|+ '''Instructions''' | |||
| Install the [https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-python.python Python extension for Visual Studio Code].|| [[Image:Language_python_vscode_install.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/f/f9/Language_python_vscode_install.png]] | |||
|- | |||
| Next, create a directory and open it in Visual Studio Code. You can do this by opening Visual Studio Code and selecting '''File > Open Folder...''' || [[Image:Language_python_vscode_newfolder.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/f/f8/Language_python_vscode_newfolder.png]] | |||
|- | |||
| Open the Command Palette (Ctrl + Shift + P), type '''Python: Create Environment''', and press Enter. Select '''Venv''' when prompted. || [[Image:Language_python_vscode_newvenv.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/a/a6/Language_python_vscode_newvenv.png]] | |||
|- | |||
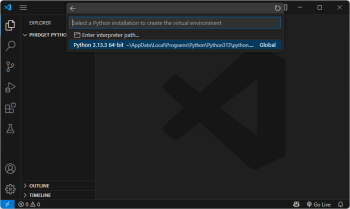
| Next, select your preferred Python interpreter from the list. You may need to browse to find it. || [[Image:Language_python_vscode_selectinterpreter.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/2/20/Language_python_vscode_selectinterpreter.png]] | |||
|- | |||
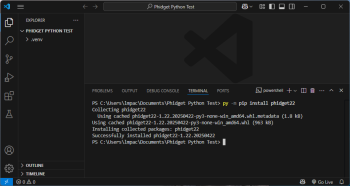
| Open a new terminal. You can do this through the Command Palette again (Ctrl + Shift + P), by typing '''Terminal: Create New Terminal'''. Install the Phidget22 pip package: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash> | |||
#Windows | |||
py -m pip install phidget22 | |||
#macOS | |||
python3 -m pip install phidget22 | |||
== | #Linux (Debian) | ||
python3 -m pip install phidget22 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|| [[Image:Language_python_vscode_installpackage.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/a/a8/Language_python_vscode_installpackage.png]] | |||
|- | |||
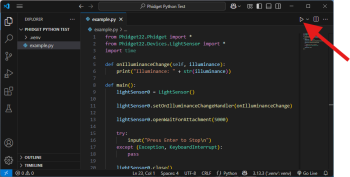
| Finally, add your Python file and run it using the button in the top right corner.|| [[Image:Language_python_vscode_runcode.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/9/96/Language_python_vscode_runcode.png]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
===PyCharm=== | |||
{| style="margin:auto;" class="table-no-border mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
|+ '''Instructions''' | |||
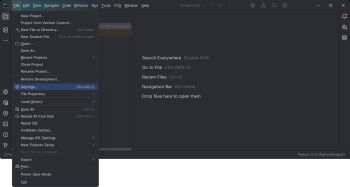
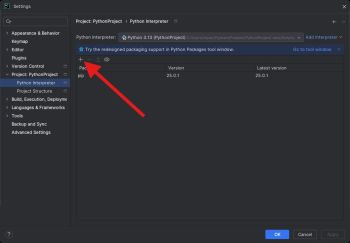
| Create your PyCharm project and navigate to '''Settings''': || [[Image:Windows_pycharm_settings.jpg|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/7/75/Windows_pycharm_settings.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
| Next, navigate to '''Project > Project Interpreter''' and click on the '''+''' symbol: || [[Image:Windows_pycharm_addpackage.jpg|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/6/6f/Windows_pycharm_addpackage.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
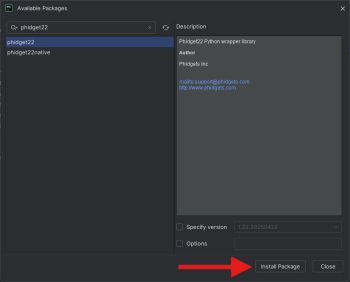
| Search for '''phidget22''' and install the package: || [[Image:Windows_pycharm_installpackage.jpg|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/a/ad/Windows_pycharm_installpackage.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
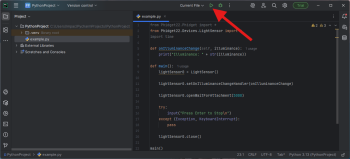
| Finally, add your Python file and run it using the button at the top of the screen: || [[Image:Windows_pycharm_run.png|center|350px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/0/0a/Windows_pycharm_run.png]] | |||
|} | |||
==Example Code== | |||
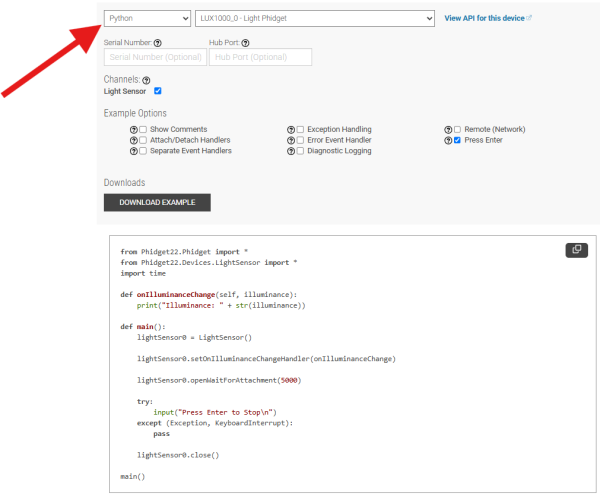
Navigate to our [https://www.phidgets.com/?view=code_samples&lang=Python Code Sample Generator] to view and download code samples that are tailored to your specific device. | |||
[[Image:Language_python_codesample.png|center|600px|link=https://cdn.phidgets.com/docs/images/2/2d/Language_python_codesample.png]] | |||
===Phidget Programming Basics=== | |||
{{PhidgetProgrammingBasicsLink}} | |||
==API== | |||
[{{SERVER}}/?view=api&lang=Python Phidget22 API] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:51, 11 June 2025
Get Started
With the Phidget22 Python library, it's easy to create Python applications that work with Phidget devices.
Python Libraries
pip Package
The Phidget22 Python library is available as a pip package. Most development environments provide built-in tools to manage packages. View the Development Environment Configuration section below for examples.
macOS Considerations
Phidget devices running a HID USB stack require the installation of the macOS libraries or the standalone Phidget Control Panel (download here).
To determine what USB stack your Phidget device is on, navigate to the product page and then to the specification tab, and look for the USB Stack specification. If you are using a VINT device, navigate to the product page for the VINT Hub you are using.
Linux Considerations
Linux restricts access to USB devices to the root user. To run your Python application as a regular user, you'll need to set up udev rules on your system.
Source Files
The Phidget22 Python library source files are available here.
Development Environment Configuration
Most development environments provide built-in tools to manage Python interpreters, packages, and virtual environments. See the examples below for more information.
Installing a Python Interpreter
If you don't already have a Python interpreter installed, you can download and install one from python.org or through package managers like Homebrew.
Visual Studio Code
| Install the Python extension for Visual Studio Code. | |
| Next, create a directory and open it in Visual Studio Code. You can do this by opening Visual Studio Code and selecting File > Open Folder... | |
| Open the Command Palette (Ctrl + Shift + P), type Python: Create Environment, and press Enter. Select Venv when prompted. | |
| Next, select your preferred Python interpreter from the list. You may need to browse to find it. | |
Open a new terminal. You can do this through the Command Palette again (Ctrl + Shift + P), by typing Terminal: Create New Terminal. Install the Phidget22 pip package:
#Windows
py -m pip install phidget22
#macOS
python3 -m pip install phidget22
#Linux (Debian)
python3 -m pip install phidget22
|
|
| Finally, add your Python file and run it using the button in the top right corner. |
PyCharm
| Create your PyCharm project and navigate to Settings: | |
| Next, navigate to Project > Project Interpreter and click on the + symbol: | |
| Search for phidget22 and install the package: | |
| Finally, add your Python file and run it using the button at the top of the screen: |
Example Code
Navigate to our Code Sample Generator to view and download code samples that are tailored to your specific device.
Phidget Programming Basics
To learn more about the structure of the example code, visit our Phidget Programming Basics guide.