Phidget Dictionary: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
Have a look at the | Have a look at the {{Phidget22API}} documentation to learn how to use these methods in the language of your choice. Select your preferred language from the first drop-down box, and select '''Dictionary API''' from the second box. | ||
Interestingly, you don't even need a Phidget to use the Dictionary! You can use our libraries and the [[Phidget Network Server]] without any Phidgets. Usually, there's not much to broadcast on the Network Server without a Phidget, but the Dictionary is the exception. With it, you'll have access to centralized key-value pair database management, pre-written, that can work across many computers on a local network. | Interestingly, you don't even need a Phidget to use the Dictionary! You can use our libraries and the [[Phidget Network Server]] without any Phidgets. Usually, there's not much to broadcast on the Network Server without a Phidget, but the Dictionary is the exception. With it, you'll have access to centralized key-value pair database management, pre-written, that can work across many computers on a local network. | ||
Revision as of 18:10, 4 May 2017
General Overview
The Phidget Dictionary is a central key-pair database for networked programs. It is a server provided by the Phidget Network Server. It allows you to store program data centrally - in the form of key-value pairs - on the same server as your Phidgets.
A Dictionary is like any other Phidget software object: You create and open it (though you don't have to wait for attachment or attach it in any way). You can subscribe to data change events, and get updates on these events from multiple devices. And when you're done, you simply close and delete it. Just like any other Phidget software object over the network, you run the functional code on your client, and the server simply runs the Phidget Network Server, which includes the Phidget Dictionary.
This works because the Network Server already maintains a centralized dictionary of key-value pairs - this is what runs the Network Server itself. We expose this data storage to you, the user, so that it can be customized and can be accessed and changed from any number of clients.
Since the Dictionary is a popular feature on our Phidget Single Board Computer (SBC), we will use that as an example. You may have already seen this image of how the Network Server works using the Phidget SBC from the Phidget Network Server page:
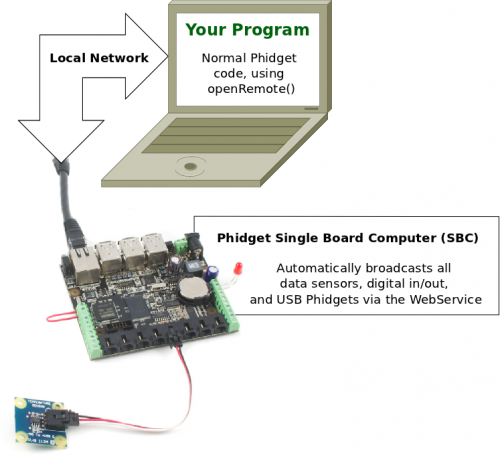
Now that we know about the Phidget Dictionary, if we were to expand the Network Server out into its components, it would look like this:
File:App guide dictionary network service flow.png
The 'Internal' Dictionary is really just the internal workings of the Phidget Network Server itself. This shares the key-value pair database with the user Dictionary. In fact, when using a dictionary object, if you catch all key events you will see ones that are produced by Phidgets! You should never modify these keys - i.e. ones that start with /PSK/ or /PCK/ - unless you want to explicitly modify Phidget-specific data. This is highly discouraged, as it’s very easy to break things; however, listening to these keys is fine if so desired.
The 'User' Dictionary is what you can build with a Phidget Dictionary object in your code. It is whatever collection of key-value pairs you might need for your network-distributed program, even if for just one computer.
At this point, you may be wondering: Why go to all the trouble of using the Dictionary? Why not just save state within your client program? Well, the Phidget Dictionary offers two advantages:
- It takes care of all database management for you - all you have to do is write pairs and listen for pair changes via events
- You don't have to write any code, it is already included in the Network Server!
Although both the Phidget Dictionary and the Network Server use the same data repository (because they are, as described in the previous paragraph, actually the same thing), you usually won't be concerned with Phidget data and will instead be creating and storing your own data to run your program with state.
The benefits above become even more useful when you have more than one client computer. This is one of the powerful aspects of the Phidget Network Server; that is, more than one computer can control Phidgets by making your system networked. In this case, having a centralized store of data that all clients can 'subscribe' to in order to act when it changes is a very powerful tool:
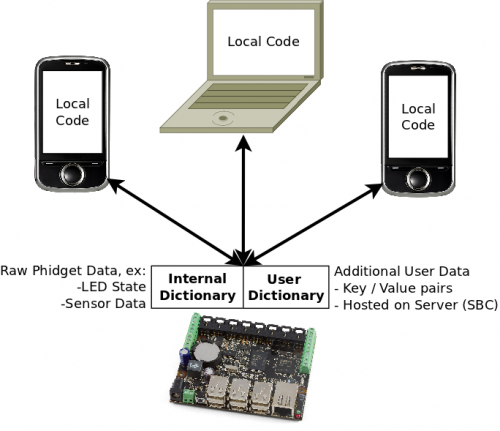
The intended use for the dictionary is as a central repository for communication and persistent storage of data between several client applications. For example, it can be used as a higher level interface exposed by one application that controls the Phidgets for others to access, rather than every client talking directly to the Phidgets themselves.
Using The Dictionary
To use the Dictionary, you would create a Dictionary object within your code, just like you would any other Phidget software object. To "listen" to changes of the value associated with a key, the Dictionary has a onFilter() (or similar) event function. The dictionary filters using extended regular expressions for key matching to execute code for specific keys. Go into the Phidget control panel and click on the 'Network Server tab and ensure the server is started and the dictionary server is enabled. Here's an example of how you might use the dictionary in a C program:
// Declare the dictionary handle
PhidgetDictionaryHandle dict;
// Create the new dictionary object using the handle
PhidgetDictionary_create(&dict);
// Open connection to the dictionary using the object, server, port, and password
PhidgetDictionary_openRemote(dict,"localhost",5662,NULL);
// Add a key-value pair to the dictionary
char *key1 = "001";
char *val1 = "first";
PhidgetDictionary_add(dict,key1,val1,0); // The last parameter is 0 if you want the pairs to clear when the object is closed, and 1 if you want them to persist
// Access and print a value from the dictionary based on a given key
char newValue[20];
PhidgetDictionary_get(dict, key1, &newValue,20); // '20' refers to the length of the buffer used to store the result
printf("Value: %s",newValue);
// Remove a pair from the dictionary based on a given key
PhidgetDictionary_remove(dict, key1);
// Close and clean up the dictionary object
PhidgetDictionary_close(dict);
PhidgetDictionary_delete(&dict);
Have a look at the Phidget22 API documentation to learn how to use these methods in the language of your choice. Select your preferred language from the first drop-down box, and select Dictionary API from the second box.
Interestingly, you don't even need a Phidget to use the Dictionary! You can use our libraries and the Phidget Network Server without any Phidgets. Usually, there's not much to broadcast on the Network Server without a Phidget, but the Dictionary is the exception. With it, you'll have access to centralized key-value pair database management, pre-written, that can work across many computers on a local network.
