Language - C Sharp Linux Mono: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Language]]{{NoTitle | [[Category:Language]]{{NoTitle}} | ||
{| | {| | ||
|style="vertical-align:middle; width: 60%;"| | |style="vertical-align:middle; width: 60%;"| | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 22 May 2019
|
Language - C# Linux with Mono Welcome to using Phidgets with C#! By using C#, you will have access to the complete Phidget22 API, including events. Mono is an open-source programming environment that aims to make Microsoft .NET applications available across all operating systems. |
Install Phidget Drivers for Linux
Before getting started with the guides below, ensure you have the following components installed on your machine:
- You will need the Phidgets Linux Drivers
Use Our Examples
One of the best ways to start programming with Phidgets is to use our example code as a guide. In order to run the examples, you will need to download and install Mono. You can do this by entering the following command in the terminal:
apt-get install mono-complete
You will also need a copy of Phidget22.NET.dll.
Now that you have Mono installed and Phidget22.NET.dll on hand, download and unpack the HelloWorld example for C#:
Note: The HelloWorld example is compatible with Mono because it does not use Windows Forms. All other C# examples use Windows Forms.
Place the example and Phidget22.NET.dll in the same folder. Your project folder should now look like this:
Finally, to compile the program, enter the following command in the terminal:
mcs Program.cs -r:Phidget22.NET.dll
An executable file will be created. Run the program using mono with the following command:
mono Program.exe
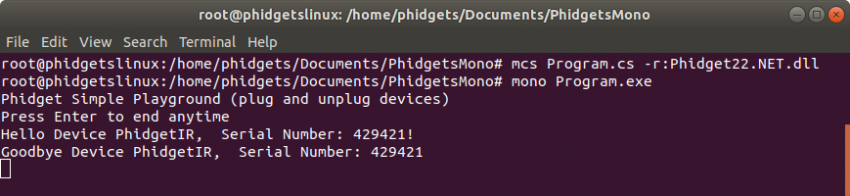
You should now have the example up and running for your device. Play around with the device and experiment with some of the functionality. When you are ready, you can edit the examples and add your own code!
Editing the Examples
With the exception of the HelloWorld example mentioned earlier, the C# examples are what comprise the Windows Phidget Control Panel. These are all graphical examples, and Mono is a non-graphical environment so you'll need to modify a few things to adapt them for your own purposes. Start with copying the contents of Form1_Load from one of the examples into your mono program's main function.
Next, you can remove the following line:
commandLineData phidgetParameters = open.parseCmdLine(); //get command line parameters
Then, you can modify any line that mentions phidgetParameters by setting it to the desired value instead of using PhidgetParameters object.
For instance:
try
{ //set all the values grabbed from command line. these values have defaults that are set in ExampleUtils.cs, you can check there to see them.
digout.Channel = phidgetParameters.Channel; //selects the channel on the device to open
digout.DeviceSerialNumber = phidgetParameters.SerialNumber; //selects the device or hub to open
digout.HubPort = phidgetParameters.HubPort; //selects the port on the hub to open
digout.IsHubPortDevice = phidgetParameters.isHubPortDevice; //is the device a port on a VINT hub?
if (phidgetParameters.isRemote) //are we trying to open a remote device?
{
digout.IsRemote = true;
Net.EnableServerDiscovery(ServerType.Device); //turn on network scan
if (phidgetParameters.Password != null && phidgetParameters.ServerName != null)
Net.SetServerPassword(phidgetParameters.ServerName, phidgetParameters.Password); //set the password if there is one
}
else
digout.IsLocal = true;
digout.Open(); //open the device specified by the above parameters
}
catch (PhidgetException ex) { errorBox.addMessage("Error opening device: " + ex.Message); }
Might become:
try
{
digout.Channel = 0;
digout.DeviceSerialNumber = 370097;
digout.HubPort = 0;
digout.IsHubPortDevice = true;
digout.IsRemote = false;
digout.Open();
}
catch (PhidgetException ex) { errorBox.addMessage("Error opening device: " + ex.Message); }
You'll also have to remove some references to graphical elements such as ErrorEventBox. If you assign event handler functions, you'll have to define them before your main function, similar to the manager events in the HelloWorld example we covered earlier.
You can then manipulate the rest of the code as your application requires. A more in-depth description of programming with Phidgets will be covered in the next section.
Setting up a New Project
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget functionality to an exisiting project, you'll need to configure your development environment to properly link the Phidget .NET library.
To include the Phidget22.NET library, simply add the following lines to your code:
using Phidget22;
using Phidget22.Events;
Place a copy of Phidget22.NET.dll in the same folder as your program. Your project folder should now look like this:

Finally, to compile the program, enter the following command in the terminal:
mcs Program.cs -r:Phidget22.NET.dll
An executable file will be created. Run the program using mono with the following command:
mono Program.exe
Success! The project now has access to Phidgets.
What's Next?
Now that you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our guide on Phidget Programming Basics to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.![]()
