1016 User Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{ugAddressingInformation}} | {{ugAddressingInformation}} | ||
{{ugUsingYourOwnProgram|This Phidget is compatible with the {{ExampleLink|CapacitiveTouch}}.}} | |||
This Phidget is compatible with the {{ExampleLink|CapacitiveTouch}}. | |||
==Technical Details== | ==Technical Details== | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 28 August 2018
Getting Started
Welcome to the 1016 user guide! In order to get started, make sure you have the following hardware on hand:
- 1016 PhidgetCircularTouch and custom USB cable
- computer
Next, you will need to connect the pieces:
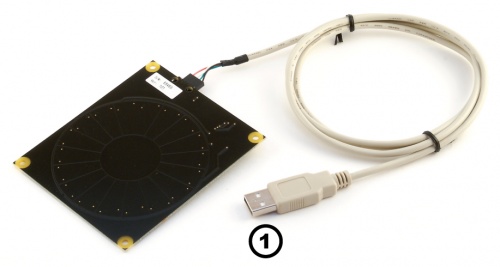
- Connect the Phidget to your computer using the USB cable
Now that you have everything together, let's start using the 1016!
Using the 1016
Phidget Control Panel
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1016, the Phidget Control Panel running on a Windows machine will be used.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines.
Windows
To open the Phidget Control Panel on Windows, find the ![]() icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
macOS
To open the Phidget Control Panel on macOS, open Finder and navigate to the Phidget Control Panel in the Applications list. Double click on the ![]() icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
For more information, take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1016.
First Look
After plugging the 1016 into your computer and opening the Phidget Control Panel, you will see something like this:
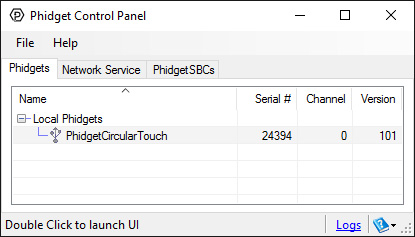
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Capacitive Touch
Double-click on the Capacitive Touch object labelled PhidgetCircular Touch in order to run the example:
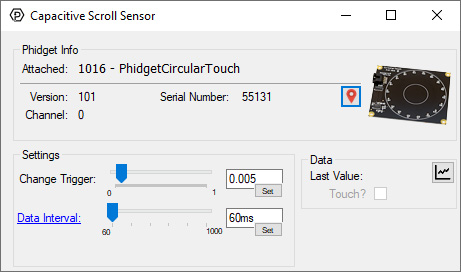
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Modify the change trigger and/or data interval value by dragging the sliders. For more information on these settings, see the data interval/change trigger page.
- The sensitivity of the 1016 can also be adjusted. The higher the sensitivity, the more susceptible the 1016 will be to sensing touch.
- When the 1016 senses a touch, the state of the Touch? checkbox will change.
- The Last Value label corresponds to the location of the last touch along the 1016.
Finding The Addressing Information
Before you can access the device in your own code, and from our examples, you'll need to take note of the addressing parameters for your Phidget. These will indicate how the Phidget is physically connected to your application. For simplicity, these parameters can be found by clicking the button at the top of the Control Panel example for that Phidget.
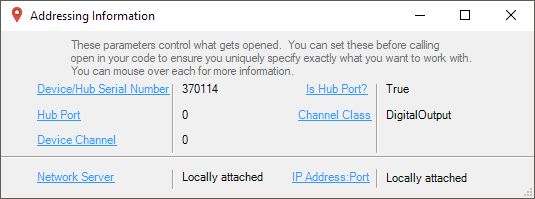
In the Addressing Information window, the section above the line displays information you will need to connect to your Phidget from any application. In particular, note the Channel Class field as this will be the API you will need to use with your Phidget, and the type of example you should use to get started with it. The section below the line provides information about the network the Phidget is connected on if it is attached remotely. Keep track of these parameters moving forward, as you will need them once you start running our examples or your own code.
Using Your Own Program
You are now ready to start writing your own code for the device. The best way to do that is to start from our Phidget is compatible with the [https://www.phidgets.com/?view=code_samples&class=CapacitiveTouch CapacitiveTouch Examples. Code Samples].
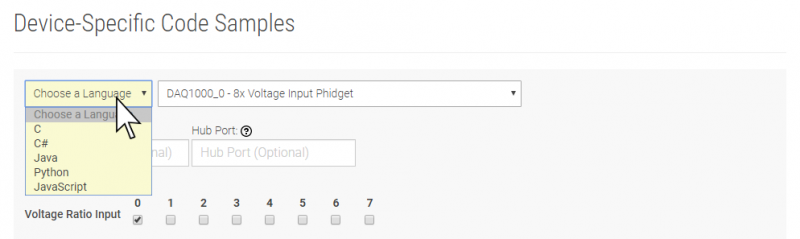
Select your programming language of choice from the drop-down list to get an example for your device. You can use the options provided to further customize the example to best suit your needs.
Once you have your example, you will need to follow the instructions on the page for your programming language to get it running. To find these instructions, select your programming language from the Programming Languages page.
Technical Details
Device Inputs
The 1016 appears to the Phidget libraries as a CapacitiveTouch object. Sliding a finger around the touch sensor varies the axis value from 0 to 1 in approximately 125 discrete steps. When the finger is removed, the final measured value is retained.
If it is desired to use the touch slider as an array of buttons, or a combination of an array of buttons and a smaller slide-touch area, one must only interpret specific sub-ranges of sensor values differently in software depending upon the intended use. If sub-ranges of values are to be used as buttons, it is recommended that a small range of sensor values be left between the sub-ranges where a null-response is observed.
Dielectric Separation
The 1016 has been left without components on the contact side so that it may be mounted behind a sheet of glass or plastic. The recommended thickness of separation material is 1/8". Silicon adhesive is recommended when attaching the Phidget to the material; standing the 1016 off or creating space between the separation material and the Phidget can cause false-triggering to occur.
It should be noted that materials thicker than 1/8" may work, but will require a larger surface area of contact to ensure proper triggering (i.e. two fingers instead of one). Increasing the surface area of the contacting object helps to increase the measurable capacitance at the point of contact that further seperation causes to reduce, balancing these factors out.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.